Sources:
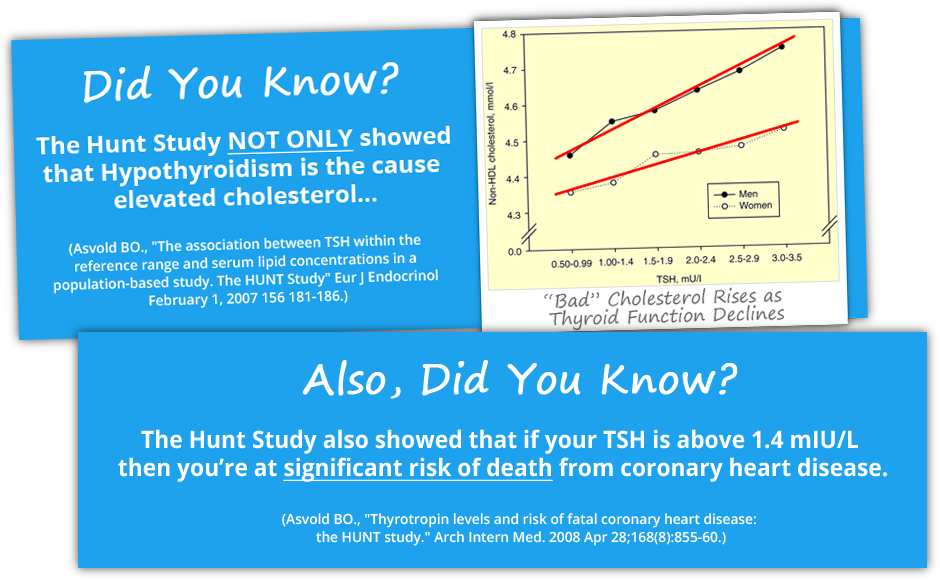
1) Asvold BO., “Thyrotropin levels and risk of fatal coronary heart disease: the HUNT study.” Arch Intern Med. 2008 Apr 28;168(8):855-60.
2) Asvold BO., “The association between TSH within the reference range and serum lipid concentrations in a population-based study. The HUNT Study” Eur J Endocrinol February 1, 2007 156 181-186.
3) Baisier, W. V., “Thyroid Insufficiency. Is Thyroxine the Only Valuable Drug?” Journal of Nutritional & Environmental Medicine. (2001), 11, 159-166.
4) Carvalho, D. P., “Thyroid peroxidase activity is inhibited by amino acids” Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 2000 Mar;33(3):355-61.
5) Fukusen N.,”Inhibition of chymase activity by phosphoglycerides.” Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 1985 Feb 15;237(1):118-23.
6) Chopra I.J., “Evidence for an inhibitor of extrathyroidal conversion of thyroxine to 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine in sera of patients with nonthyroidal illnesses.” The journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 1985 Apr;60(4):666-72.
7) Tabachnick M., “Effect of long-chain fatty acids on the binding of thyroxine and triiodothyronine to human thyroxine-binding globulin.” Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1986 Apr 11;881(2):292-6.
8) Wiersinga W.M., “Inhibition of nuclear T3 binding by fatty acids.” Metabolism. 1988 Oct;37(10):996-1002.
9) Rafael J. “The effect of essential fatty acid deficiency on basal respiration and function of liver mitochondria in rats.” The journal of nutrition. 1984 Feb;114(2):255-62.
10) Fery, F., “Hormonal and metabolic changes induced by an isocaloric isoproteinic ketogenic diet in healthy subjects.” Diabetes and Metabolism. 1982 Dec;8(4):299-305.
11) Orzechowska-Pawiłojć, A., “The influence of thyroid hormones on homocysteine and atherosclerotic vascular disease” Endokrynol Pol. 2005 Mar-Apr;56(2):194-202.
12) Ramsden C.E., “Use of dietary linoleic acid for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease and death: evaluation of recovered data from the Sydney Diet Heart Study and updated meta-analysis.” BMJ. 2013 Feb 4;346:e8707.
13) Shering, SG., “Thyroid disorders and breast cancer.” Eur J Cancer Prev. 1996 Dec;5(6):504-6.
14) Ratcliffe, J. G.,”Thyroid function in lung cancer” Br Med J. Jan 28, 1978; 1(6107): 210–212.
15) Turken, O.,”Breast cancer in association with thyroid disorders.” Breast Cancer Res. 2003;5(5):R110-3. Epub 2003 Jun 5.
16)Linos, A. “Does coffee consumption protect against thyroid disease?” Acta chirurgica Scandinavica. 1989 Jun-Jul;155(6-7):317-20.
17) Petrek, J.A., “The inhibitory effect of caffeine on hormone-induced rat breast cancer” Cancer. 1985 Oct 15;56(8):1977-81.
18) Nakanishi, N. “Effects of coffee consumption against the development of liver dysfunction: a 4-year follow-up study of middle-aged Japanese male office workers.” Industrial Health. 2000 Jan;38(1):99-102.
19) Freedman, Neal D. “Association of Coffee Drinking with Total and Cause-Specific Mortality” New England Journal of Medicine. 2012; 366:1891-1904.
20) Nauman A., “The Effect of Adrenaline Pretreatment on the In Vitro Generation of 3,5,3′-Triiodothyronine and 3,3′,5′-Triiodothyronine (Reverse T3) in Rat Liver Preparation” Hormone and metabolic research. 1984 Sep;16(9):471-4.
21) Heyma P., “Glucocorticoids decrease in conversion of thyroxine into 3, 5, 3′-tri-iodothyronine by isolated rat renal tubules.” Clin Sci (Lond). 1982 Feb;62(2):215-20.
22) Laugero K.D., “A new perspective on glucocorticoid feedback: relation to stress, carbohydrate feeding and feeling better.” J Neuroendocrinol. 2001 Sep;13(9):827-35.
23) Konno N., “Association between dietary iodine intake and prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism in the coastal regions of Japan.”The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 1994 Feb;78(2):393-7.
24) Zois C., “High prevalence of autoimmune thyroiditis in schoolchildren after elimination of iodine deficiency in northwestern Greece.” Thyroid. 2003 May;13(5):485-9.
25) Harach H.R., “Thyroid carcinoma and thyroiditis in an endemic goitre region before and after iodine prophylaxis.” Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1985 Jan;108(1):55-60.
26) Wémeau JL., “Hypothyroidism related to excess iodine.” Presse Médicale. 2002 Oct 26;31(35):1670-5.
27) Ruwhof C., “Iodine and thyroid autoimmune disease in animal models.” Thyroid. 2001 May;11(5):427-36.
28) Himmelstein DU., “Medical bankruptcy in the United States, 2007: results of a national study.” Am J Med. 2009 Aug;122(8):741-6.
![]()
































 We work with clients of every age and way of life from children to busy executives. These 5 lifestyle plans hold the keys that we use with our clients to make the transition into the system easy and seamless. Some clients are busy and always on the go, some are coming from very damaging diets, others are looking for budget-friendly ideas, and some are just more comfortable taking things at their own pace. Either way, we have you covered. (20 pages, 5 digital mini e-books).
We work with clients of every age and way of life from children to busy executives. These 5 lifestyle plans hold the keys that we use with our clients to make the transition into the system easy and seamless. Some clients are busy and always on the go, some are coming from very damaging diets, others are looking for budget-friendly ideas, and some are just more comfortable taking things at their own pace. Either way, we have you covered. (20 pages, 5 digital mini e-books).
 Maybe you’ve heard the proverb, “Give a man a fish and you feed him for a day. Teach a man to fish and you feed him for a lifetime”. While we’ve given you the fish and have done everything imaginable to make this as easy and thoughtless as possible… I also believe in teaching you how to fish by giving you the power and knowledge to create your own strategically balanced meals using our Strategic Thyroid Balance Principle. My Advanced Diet Planning Guide does just that. And you’ll have access to my personal diet calculators to ensure that your entire diet is strategically balanced for maximum thyroid function. (14 page digital e-book and 3 Excel calculators).
Maybe you’ve heard the proverb, “Give a man a fish and you feed him for a day. Teach a man to fish and you feed him for a lifetime”. While we’ve given you the fish and have done everything imaginable to make this as easy and thoughtless as possible… I also believe in teaching you how to fish by giving you the power and knowledge to create your own strategically balanced meals using our Strategic Thyroid Balance Principle. My Advanced Diet Planning Guide does just that. And you’ll have access to my personal diet calculators to ensure that your entire diet is strategically balanced for maximum thyroid function. (14 page digital e-book and 3 Excel calculators). Let’s face it. You could go out and buy any book on hypothyroidism yet is the author going to make sure you understand everything and follow things correctly? Of course not, unless that author is me. I want to leave you with the best experience of your life. To go that extra mile, you’ll be receiving regular coaching emails to motivate you, hold you accountable, and answer any questions you might have along the way to ensure your success. (60+ days of emails sent directly to your inbox) This is something that many of my clients gladly pay $197 per month for this extra V.I.P. treatment.
Let’s face it. You could go out and buy any book on hypothyroidism yet is the author going to make sure you understand everything and follow things correctly? Of course not, unless that author is me. I want to leave you with the best experience of your life. To go that extra mile, you’ll be receiving regular coaching emails to motivate you, hold you accountable, and answer any questions you might have along the way to ensure your success. (60+ days of emails sent directly to your inbox) This is something that many of my clients gladly pay $197 per month for this extra V.I.P. treatment.